Connecting a VPC to a corporate network via Direct Connect
In this article:
Connecting a VPC to a corporate network via Direct Connect#
A transit gateway can be used to exchange traffic between a VPC and corporate network through a Direct Connect gateway and to inspect traffic between them and the Internet.
Hint
It is recommended that you first read the tutorial for interconnecting two VPCs in order to understand, through a simple example, which path the traffic follows from the source to the destination.
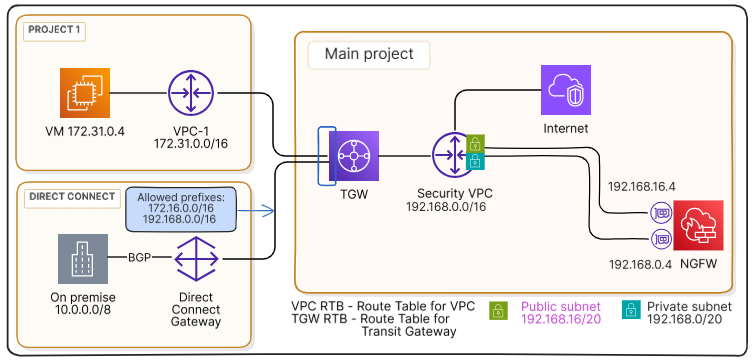
In this example, both the transit gateway (TGW) and Direct Connect gateway (DCGW) are in the main project. In addition to the DCGW, a VPC (vpc-1, 172.31.0.0/16) from another project is attached to the transit gateway. The VPC and the corporate network (10.0.0.0/8) can exchange traffic between each other and with the Internet.
All traffic is routed for inspection to a dedicated VPC (vpc-s, 192.168.0.0/16), where a virtual security appliance (NGFW) is deployed. The vpc-s is in the same project as the gateways and is connected to the Internet (i.e. has an Internet gateway).
The instance with the NGFW has two network interfaces attached: 192.168.0.4 in the private subnet 192.168.0.0/20 for communication with the VPC and corporate network, and 192.168.16.4 in the public subnet 192.168.16.0/20 for communication with the Internet.
Subnets in vpc-1 are associated with the main route table of this VPC – vpc-rtb-1. Attachment subnets in vpc-s are associated with the route table vpc-rtb-a. The private subnet 192.168.0.0/20 (the one, to which the NGFW interface 192.168.0.4 is attached) is associated with the route table vpc-rtb-s, while the public subnet 192.168.16.0/20 (the one, to which the NGFW interface 192.168.16.4 is attached) is associated with the route table vpc-rtb-i.
In addition, the transit gateway attachments to vpc-1 and Direct Connect gateway are associated with the default association route table – tgw-rtb-a, while the transit gateway attachment to vpc-s is associated with the default propagation route table – tgw-rtb-p.
Important
In this scenario, to provide access via an Elastic IP address, you need to:
create a network interface in a public subnet that is connected to the NGFW;
allocate an Elastic IP address and associate it with the created network interface;
associate the private IP address of the network interface with the NGFW as an alias or configure Proxy ARP for it;
specify a NAT rule on the NGFW to forward traffic, targeted to this private IP address, to the private IP address of the target instance.
Important
Below it is assumed that you have already:
The general procedure is as follows:
associate the Direct Connect gateway with the transit gateway;
provide access for another project and attach vpc-1 to the transit gateway;
configure routing to vpc-s on the transit gateway attachments to vpc-1 and DCGW to forward traffic to
vpc-sfor inspection;set the route to NGFW in the route table of the attachment subnets in vpc-s;
set the return route from vpc-s through the transit gateway;
configure routing on the vpc-s attachment to route traffic to
vpc-1and corporate network.
Create a transit gateway#
Note
The gateway will be created along with a default association route table tgw-rtb-a, while a default propagation route table tgw-rtb-p will be created separately and then associated with the transit gateway attachment to vpc-s.
Go to Interconnect Transit gateways and open the subsection of the same name.
Click Create.
Clear the checkbox Create route table and set it as default for::
route propagation.
Click Create to create the gateway.
Connect DCGW to TGW#
Create an association between the Direct Connect gateway and the transit gateway.
Go to Interconnect section Direct Connect Gateways.
In the resource table, select the Direct Connect gateway and click Create association.
In the window that opens, select the transit gateway with which you want to establish an association. In the Allowed prefixes field, specify the addresses of
vpc-1andvpc-s(172.31.0.0/16и192.168.0.0/16).Once the parameters are set, click Create.
As a result of the association, an attachment to the transit gateway will be created in all availability zones.
Create attachment subnets#
In each availability zone, it is recommended to create an attachment subnet to which the transit gateway will be attached. If a subnet with instances is directly attached to a transit gateway, traffic from the gateway will flow to the instances directly and thus bypass a Network ACL. With an attachment subnet, traffic between the transit gateway and other subnets in this VPC always passes through the virtual router of the VPC and is therefore filtered by the Network ACL.
Note
Security group rules apply to the traffic on network interfaces in any case, even if the instance is located in the attachment subnet.
The attachment subnet is not recommended for placement of other resources, because it is intended only for communication with the transit gateway. Therefore, to use the least address space, the smallest possible IP subnet (/28) can be allocated as an attachment subnet.
Switch to the project where the
vpc-1is located. This may require logging out of the cloud’s web interface and logging again using an account with the appropriate privileges.Go to Virtual machines Networking Subnets and click Create.
In the subnet dialog window, set the following parameters:
vpc-1.(Optional) Name tag.
Subnet address
172.31.255.0/28.Availability zone to which the transit gateway should be attached.
If you need to set additional tags, go to the next step by clicking Add tags.
After setting all the required parameters, click Create subnet.
If there is only one availability zone in the region, create subnet 192.168.255.0/28 in the vpc-s in a similar way.
If there are three availability zones in the region, create the subnets 172.31.255.16/28 and 172.31.255.32/28 in the remaining availability zones in vpc-1 and the subnets 192.168.255.0/28, 192.168.255.16/28 and 192.168.255.32/28 in the three availability zones in vpc-s. The value of 255 in the third octet of the attachment subnet addresses is chosen to ensure that the VPC address space remains cohesive, contiguous, and sufficient for accommodating subnets with instances.
You can choose the number of availability zones where you are going to create subnets: one, two or three. However, for production infrastructures, we recommend creating attachment subnets in all availability zones beforehand, as you won’t be able to change them later, but have to create the transit gateway infrastructure from scratch again.
Attach a VPC from another project to the TGW#
To be able to attach a VPC in another project to the TGW, you must grant access thereto for such a project.
Go to Interconnect Transit gateways and open the subsection of the same name.
Select the transit gateway in the resource table.
Click Set access.
In the window that opens, specify the project in the Grant access for projects field as follows: project@customer.
Click Apply.
To create an attachment, go to the project where the VPC is located. This may require logging out of the cloud’s web interface and then logging back in under a user account having permissions to this project.
Important
We recommend attaching the transit gateway to all availability zones. Once an attachment is created, you will not be able to modify the attached subnets or attach any other subnet.
Go to Interconnect Transit gateways Attachments.
Click Create.
In the window that opens, set the following parameters:
The Name tag to identify the attachment, for example,
vpc-1(optional).The transit gateway in the main project.
vpc-1.The attachment subnets in
vpc-1, to which the transit gateway will be attached.172.31.255.0/28;172.31.255.16/28;172.31.255.32/28.
In each of these subnets, a virtual network interface will be created for attachment.
Click Create to create the attachment.
Once vpc-1 is attached, go back to the main project and create a vpc-s attachment in the same availability zones.
Set up routing from vpc-1 via TGW#
All outbound traffic from vpc-1 must be forwarded to the transit gateway to be further routed to vpc-s for inspection. Below it is assumed that all subnets in vpc-1 from which traffic should be transmitted outward are associated with the main route table vpc-rtb-1. If any subnet has another route table associated, then a route via the transit gateway must also be added to that table.
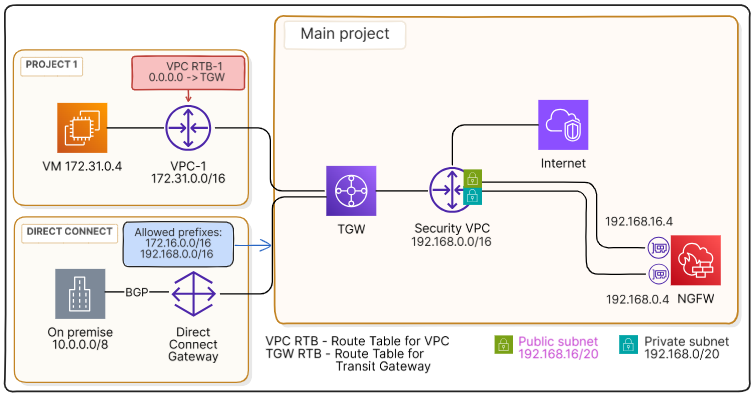
Go to Virtual machines Networking Route tables.
In the resource table, select the main route table of
vpc-1and click on the route table ID to go to its page.Open the Routes tab and click Add.
In the dialog window:
In the Network field, specify the target subnet
0.0.0.0/0.In the Gateway Type field, select Transit Gateway.
In the Gateway field, select the transit gateway you are using.
Click Add to create the route.
Configure routing for attachments to vpc-1 and DCGW#
The tgw-rtb-a route table, created together with the transit gateway, was selected as the default association route table. It is automatically associated with all transit gateway attachments, including association with the DCGW (as well as the transit gateway attachment of vpc-s, but the latter will subsequently be associated with another route table – tgw-rtb-p). For the transit gateway to forward all outbound traffic from vpc-1 and DCGW for inspection, set up routes to vpc-s.
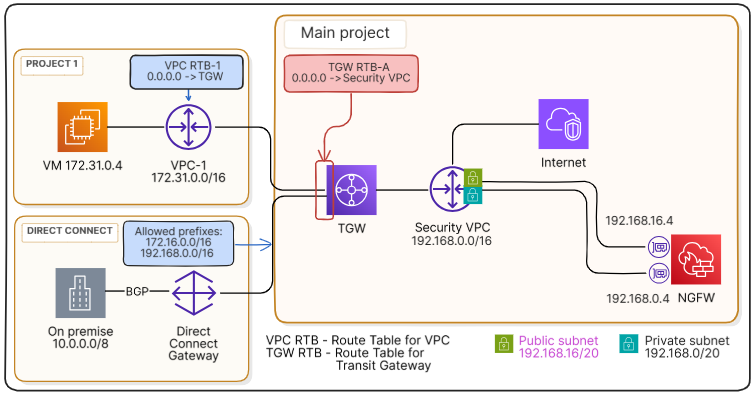
Go to Interconnect Transit gateways Route tables.
In the resource table, select the default association route table of the transit gateway and click on the route table ID to go to its page.
In the Routes tab click Add.
In the dialog window:
In the Network field, specify
0.0.0.0/0.In the Attachment field, select the attachment through which
vpc-sis attached to the transit gateway.
Click Create.
Set the route to NGFW#
All traffic coming from vpc-1 and the corporate network to the attachment subnets in vpc-s must be forwarded to the NGFW network interface (192.168.0.4) for further inspection. To do this, create a separate route table vpc-rtb-a, associate it with the attachment subnets and set up a route to the NGFW in this table.
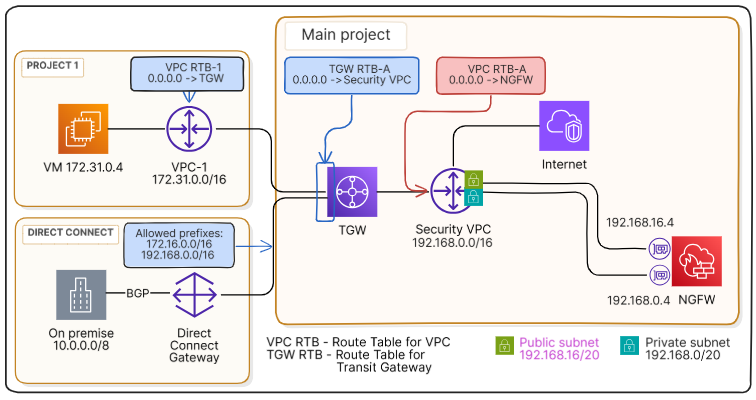
Go to Virtual machines Networking Route tables.
Associate the created route table with attachment subnets in vpc-s.
In the resource table, select the created route table and click on the table ID to go to its page.
Open the Routes tab and click Add.
In the dialog window:
In the Network field, specify
0.0.0.0/0.In the Gateway type field, select
Instance.In the Gateway field, select from the drop-down list the instance with interface 192.168.0.4, where the NGFW is running.
Click Add to create the route.
Specify routes to the Internet from vpc-s#
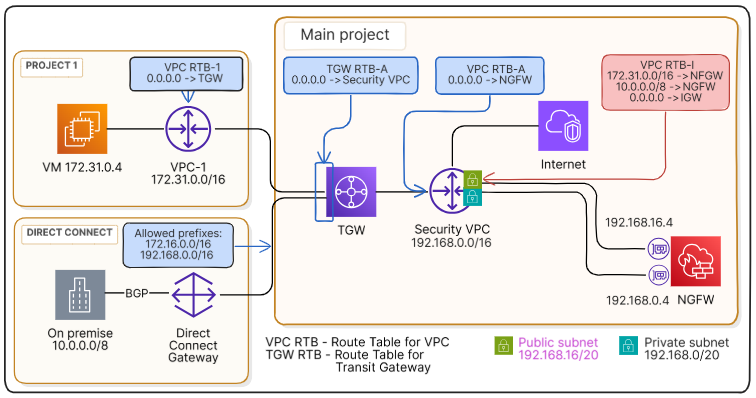
The NGFW connects to the public subnet 192.168.16.0/20 via the interface 192.168.16.4. For this subnet, you need to configure traffic routing to/from the Internet in the vpc-rtb-i route table.
Go to Virtual machines Networking Route tables.
Associate the created route table with the public subnet in vpc-s.
In the resource table, select the created route table and click on the table ID to go to its page.
Open the Routes tab and click Add.
To route traffic to the Internet, do the following in the window that opens:
In the Network field, specify
0.0.0.0/0;In the Gateway type field, select Standard Internet gateway.
Click Add to create the route.
Click Add again. To inspect inbound traffic from the Internet to
vpc-1, do the following in the window that opens:In the Network field, specify
172.31.0.0/16.In the Gateway type field, select
Instance.In the Gateway field, select from the drop-down list the instance with interface 192.168.16.4, where the NGFW is running.
Click Add to create the route.
Click Add again. To inspect inbound traffic from the Internet to the corporate network, do the following in the window that opens:
In the Network field, specify
10.0.0.0/8.In the Gateway type field, select
Instance.In the Gateway field, select from the drop-down list the instance with interface 192.168.16.4, where the NGFW is running.
Click Add to create the route.
Specify the return route from vpc-s through the transit gateway#
In the vpc-rtb-s route table associated with the private subnet 192.168.0.0/20, to which the NGFW network interface 192.168.0.4 is attached, specify routes to vpc-1 and DCGW.
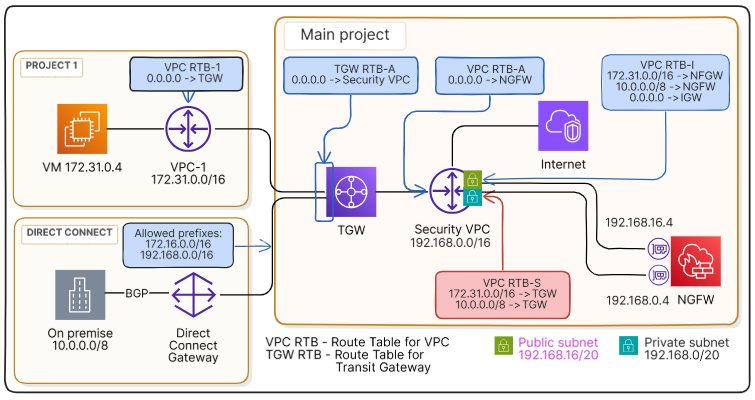
Go to Virtual machines Networking Route tables.
Associate the created route table with the private subnet in vpc-s.
In the resource table, select the created route table in
vpc-sand click on the route table ID to go to its page.In the Information tab, click the route table ID in the relevant field.
Open the Routes tab and click Add.
In the dialog window:
In the Network field, specify the target network in
vpc-1. In this example, this is network172.31.0.0/16, which corresponds tovpc-1.In the Gateway Type field, select Transit Gateway.
In the Gateway field, select the transit gateway you are using.
Click Add to create the route.
Repeat steps 4-6 to set up a route to the corporate network (in this example, its address is
10.0.0.0/8).
Configure routing via the attachment to vpc-s#
To forward inspected traffic to target VPCs, configure the transit gateway route table tgw-rtb-p for the attachment to vpc-s. To automatically add routes to other VPCs, it is recommend to set this table as default for route propagation.

Go to Interconnect Transit gateways Route tables.
In the resource table, select the created route table and click on the table ID to go to its page.
In the Route propagation tab, click Enable propagation. In the window that opens, select the transit gateway attachments to
vpc-1and DCGW. Click Enable. Routes tovpc-1and corporate network through DCGW will be added to the route table.Go to Interconnect Transit Gateways Transit Gateways and set the table as default for route propagation. Routes to all subsequently attached VPCs will be automatically added to this table.
Go to Interconnect Transit gateways Route tables and associate this route table with transit gateway attachment to vpc-s.
The created default propagation route table tgw-rtb-p will be associated with the attachment to vpc-s instead of tgw-rtb-a, a default association route table. Routes through the transit gateway to vpc-1 and the corporate network, as well as to all subsequently attached VPCs, will be installed in this table automatically.